The Military Satellite Market
by Omkar Nikam
Strasbourg, France, September 6, 2021--Military operations have integrated satellite technology as a crucial part of their operations on land, air, and sea for over half a century. And the United States is one of the leading countries followed by Russia and several European nations in boosting space applications for military. But the world is slowly shifting from a US centric sphere, primarily due to ease in accessibility of resources, increased cooperation between non-allied nations, and rapid innovation the technological sector.
The inception of the United States Space Force (USSF) in December 2019 has proved to be a turning in the global military satellite segment. With an annual budget of more than US$17bn USSF is slowly becoming a central engine of enhancing military assets in space. While developed countries like France already have a Space Force established before the USA, the space fairing nations like India and China are also trying to amplify their space applications for military. While considering the global acceleration of satellite applications in the military domain, the New Space has been one of the crucial sectors to reduce the cost and make space more accessible to both commercial and military agencies. As the world progresses towards a nexus of challenges thrown up from variety of issues, the development of satellite applications will be crucial for military agencies. To dissect this major shift of government agencies towards integrating satellite applications in the military domain, we will tap on some of the critical points that will set a new course for the satellite industry
Enhancing Communications, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance with New Space Technologies
Satellites are the backbone of communication, reconnaissance, and surveillance in the modern warfare and according to GlobalData, the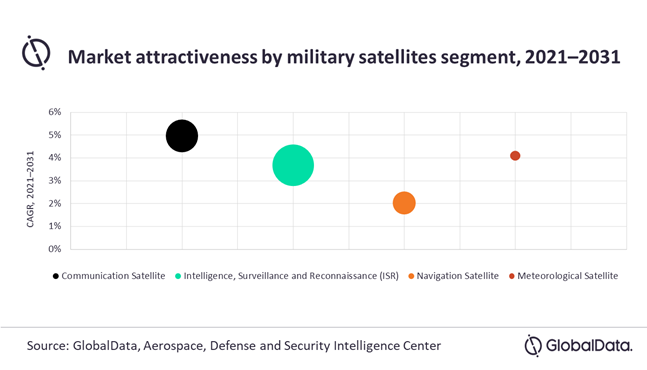 intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) market segment is expected to reach US$ 7 Billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.67% during 2021-2031. The New Space technologies have proven that commercial companies can reduced the high defense budgets by enhancing security capabilities using new space applications. Companies like SpaceX are the result of National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) commercial space initiatives which has proven over time that the entry of private and commercial entities can significantly reduce the cost of accessing space applications.
intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) market segment is expected to reach US$ 7 Billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.67% during 2021-2031. The New Space technologies have proven that commercial companies can reduced the high defense budgets by enhancing security capabilities using new space applications. Companies like SpaceX are the result of National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) commercial space initiatives which has proven over time that the entry of private and commercial entities can significantly reduce the cost of accessing space applications.
 intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) market segment is expected to reach US$ 7 Billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.67% during 2021-2031. The New Space technologies have proven that commercial companies can reduced the high defense budgets by enhancing security capabilities using new space applications. Companies like SpaceX are the result of National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) commercial space initiatives which has proven over time that the entry of private and commercial entities can significantly reduce the cost of accessing space applications.
intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) market segment is expected to reach US$ 7 Billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.67% during 2021-2031. The New Space technologies have proven that commercial companies can reduced the high defense budgets by enhancing security capabilities using new space applications. Companies like SpaceX are the result of National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) commercial space initiatives which has proven over time that the entry of private and commercial entities can significantly reduce the cost of accessing space applications.
Similarly, in Europe, the European Union Agency for the Space Programme’s (EUSPA) Government Satellite Communications (GOVSATCOM) initiative will accelerate the research and innovation in the EU’s Common Security and Defence Policy (CSDP). Considering these efforts of developed nations, New Space technologies will help government and military agencies counter hybrid threats in the coming years.
On the other hand, advancement of space technology and low-cost services are some of the crucial factors that have urged many developing nations to equip their defense forces with space applications. Though dropping prices of satellite services is one of the reasons for increasing the demand for military space applications, the fast-track need for upgrading the defense technology is the most important factors for many developing nations. Especially considering the military intelligence operations, Geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) plays a central role in the intelligence nexus. And as companies like Planet Labs, Digital Globe have paved the way for innovative and low-cost satellite imagery services, the road to space applications for military will encourage numerous public-private partnerships (PPPs) in the near future.
Privatization and International Cooperation: Rise of New Allies
Though the defense industry’s commercial outlook has made space a peaceful resource; many developing countries are still struggling to provide appropriate opportunities for the private sector in the defense segment. So, what is the end solution to accelerate the research and development process for military space applications? Encourage more private engagements by targeting technology niche is one of way to expedite this process. For example, in 2015, China became of the countries that opened its door for private players to engage in military space developments. Similarly, the USA displays an excellent example of how encouraging PPPs can lead to the overall socio-economic growth of the country. Therefore, privatization is one of the ways to bring-in innovation and harness the right talent for the nation.
Following the global trend of privatization in the space industry, the international affairs might create a series of barriers when deploying or initiating a satellite application of military interest. The international relations between nation have by far impacted every commercial industry, as it heavily relies on shifting gears with respect to geopolitics. And as satellite industry is racing towards serving the government and military needs, it will potentially change the future landscape of international cooperation in the industry. For example, India and USA are slowly becoming strong partners and this international cooperation will prove beneficial for both the nations to enhance their existing partnerships in the satellite sector; but will also push away some of their partners to initiate cooperation with new allies.
Emerging Technologies
Numerous things are rapidly changing the technological landscape of the military satellite applications, but the recent success of Chinese Quantum Communication satellite lies at the forefront of the defense industry. With this success, China will be able to change the face of Signal Intelligence (SIGINT). In SIGINT, there is a high probability of third-party penetration by using various hacking techniques. And Considering the cyber-attacks, the satellite industry is progressing to counter the cyber threats via strengthening the end-to-end encryption techniques. But this scenario is about to change with the inception of Quantum Communication satellites. China is not the only country looking beyond skies to deploy Quantum Communication network; India, South Korea, Singapore, and Japan are also the upcoming players who are looking forward or have already made some amounts of investments in Quantum Communication network via satellite. Arqit, a UK-based startup, is one of the emerging companies pioneering secure communication technique by utilizing quantum key distribution (QKD). The company has recently raised US$400mn through Special Purpose Acquisition Company (SPAC). Such startups can prove to be beneficial partners for government and military agencies, as the world is entering an era hybrid threats.
Similarly, multi-domain war operations will also require cutting technologies to ensure smooth operation on the field. SES is one of the pioneers in the ISR segment, the company has been one of the strong partners of several agencies. And with the GovSat (a public-private joint venture company between the Luxembourg Government and SES), the company will create a strong foundation to enhance Europe’s ambitious plans for secure communications in space. The cyber-attacks have paved way for hybrid threats and satellite industry can fill this gap by serving the needs of government and military agencies.
Conclusion
As the military demand continues push the boundaries of innovation, satellite industry should tap into emerging technologies like quantum satellite communications and keep a close eye on enhancing cyber security. Considering the changing climate of international affairs and current landscape of conflicts around, it is by far safe to say that satellite industry will have the opportunity to present new technologies to help government and military agencies to counter hybrid threats.
Every technology upgrade brings more comfort to society, but its very strength also invites challenge. This is one of the reasons why space is a point attraction for many nations around the world. But, tracking the global footprints of the space applications for the defense industry, both developing and developed nations have started looking towards space as a valuable asset for national security as well as to ensure the economic growth of the country.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 Omkar Nikam is is an independent space and satellite consultant based in Strasbourg, France. He has eight years of experience in technology and business consulting. He is also the EMEA correspondent for Satellite Markets & Research, USA. Omkar specializes in market research, analysis, and consulting services for several space and satellite market verticals. He can be reached at: www.oknikam.com
Omkar Nikam is is an independent space and satellite consultant based in Strasbourg, France. He has eight years of experience in technology and business consulting. He is also the EMEA correspondent for Satellite Markets & Research, USA. Omkar specializes in market research, analysis, and consulting services for several space and satellite market verticals. He can be reached at: www.oknikam.com





